Introduction
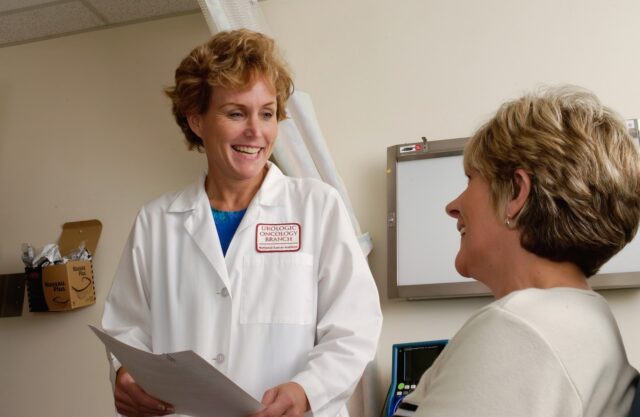
Data security in healthcare software is paramount in an age where the digital transformation of the healthcare industry is rapidly accelerating.
As the healthcare sector increasingly relies on technology for patient records, the volume of sensitive and confidential patient information being stored and transmitted electronically has grown exponentially.
The consequences of failing to secure healthcare data are profound. It encompasses the potential compromise of patients’ personal and medical information.
Furthermore, the ethical obligations to protect the privacy and confidentiality of patient data are deeply rooted in the healthcare profession.
This article sets the stage for a comprehensive exploration of the critical issues surrounding data security in healthcare software.
Here, we will cover everything from the latest encryption techniques to compliance with regulatory standards and the evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats.
The Significance Of Healthcare Data Security
Patient data is a treasure trove of sensitive and confidential information, including medical histories, treatment plans, test results, and personal identifiers. Protecting this data is a legal and ethical obligation and crucial for maintaining trust between patients, healthcare providers, and software developers.
Balancing Privacy And Confidentiality
Balancing privacy and confidentiality can be challenging, especially when there is a need to share sensitive information, such as in healthcare or legal proceedings.
Striking the right balance often requires:
- Informed Consent: Individuals should be well-informed about how their information will be used and shared and consent to these actions.
- Legally Established Protections: Laws and regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in healthcare or attorney-client privilege in law, establish a framework for maintaining confidentiality.
- Data Security Measures: Implementing robust data security measures, including encryption and access controls, can help protect sensitive information.
- Ethical Practices: Professionals and organizations should adhere to ethical standards and best practices for handling confidential information.
Legal And Regulatory Compliance
Legal and regulatory compliance refers to the adherence to established laws, regulations, and industry standards within a specific jurisdiction or industry.
It is a fundamental responsibility for individuals, organizations, and businesses to operate within the boundaries set by applicable legal frameworks, ensuring that their actions and practices align with the requirements and expectations stipulated by governing authorities.
Compliance measures are implemented to maintain ethical conduct, protect stakeholders, and prevent legal violations or penalties.
In various sectors, from healthcare to finance and environmental protection, strict compliance is a legal obligation and a means to foster transparency, safety, and public trust.
Reputation And Trust
Reputation and trust are intangible yet invaluable assets that profoundly influence personal relationships, business interactions, and overall societal well-being.
A positive reputation is built on honesty, reliability, and ethical conduct, leading to trust between individuals, organizations, and communities.
Trust, in turn, enables cooperation, collaboration, and the smooth functioning of society. A strong reputation is a currency of credibility, fostering confidence in one’s character, products, or services.
It is essential in decision-making processes, influencing choices ranging from selecting service providers to investment opportunities.
Preserving reputation and trust is a moral imperative and a pragmatic strategy for long-term success and harmonious social interactions.
If your healthcare services lack the necessary software, seek help from the healthcare software development – Jelvix.
Cybersecurity Threats
The digital age has given rise to an array of cybersecurity threats, each potentially compromising the security of patient data:
Data Breaches
Data breaches occur when unauthorized individuals gain access to patient records. These breaches can occur through hacking, employee negligence, or physical hardware theft, such as laptops or smartphones.
Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware attacks involve encrypting data and demanding a ransom for its release. Healthcare organizations are often targeted due to the critical nature of their data.
Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks use deceptive tactics, like fraudulent emails, to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information. These attacks can be difficult to detect and prevent.
Data Security Best Practices
To combat these threats and ensure the security of patient information, healthcare organizations and software developers should implement several best practices:
Encryption
- Data At Rest: Encryption of data at rest means that information is protected when it is stored on servers, databases, or physical devices. This encryption ensures that even if someone gains unauthorized access to the storage medium, they cannot decipher the data without the encryption key.
- Data In Transit: Encryption of data in transit secures information as it travels between different points, such as when it is transmitted over a network or accessed via the internet. This safeguard prevents interception and eavesdropping during transmission, ensuring the data remains confidential.
Access Control
Implementing access controls involves setting up permissions and restrictions. These restrictions and permissions determine who can access, view, and modify patient records.
Access should be granted based on roles and the principle of least privilege. This means users only have access to the data necessary for their specific job responsibilities. This practice minimizes the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Regular Audits And Training
Regular security audits involve assessing the entire healthcare software system for vulnerabilities, compliance with regulations, and adherence to security policies. Audits help identify weaknesses that can be addressed promptly.
Providing ongoing training to staff is essential. Employees should be educated on cybersecurity best practices and aware of the latest threats, tactics, and trends in data security.
Training empowers them to recognize potential risks and respond appropriately, enhancing the overall security posture.
Backup And Disaster Recovery
Maintaining regular data backups ensures that critical patient information is continuously saved to a secure location.
In the event of a data breach, system failure, or any other unforeseen disaster, these backups can be used to restore lost or compromised data.
A disaster recovery plan outlines the steps and procedures to follow during such emergencies, ensuring the timely recovery of data and system functionality.
Secure Software Development
Security should be a priority from the beginning of the software development process. This includes identifying potential security risks, conducting security assessments, and implementing security.
Continuous testing and monitoring are essential to identify and rectify vulnerabilities as the software evolves.
Compliance With Regulations
Healthcare organizations, particularly in the United States, are bound by regulations such as HIPAA. It sets strict standards for data protection, privacy, and security. Compliance with these regulations is not optional but mandatory.
Regular assessments, audits, and internal reviews are vital to identify gaps in compliance and address them promptly to avoid legal and financial consequences.
The Future Of Healthcare Data Security
Data security will remain an ever-evolving challenge as the healthcare industry embraces digital technologies.
Adopting emerging technologies like blockchain and advanced authentication methods may provide additional layers of protection.
Healthcare organizations and software developers must remain adaptable and proactive in their approach to data security.
In conclusion, the digital age has ushered in a new era of healthcare where data security is paramount. Safeguarding patient information is not only a legal requirement but also a moral obligation.